Bitcoin - Overview
Description
Bitcoin is the most famous digital currency of our times. It enables its users to transfer money instantly to anyone in the world.It is decentralized, this means that there is no central authority controlling the transactions and issuing new money, but it’s maintained via a collective and distributed effort.Each currency unit is called bitcoin and they are, like real money, scarce (there’s a limited amount), divisible, portable, difficult to counterfeit and cannot be spent twice.Bitcoin is based on public-private key cryptography. Whoever has the private key (like a password) linked to an address (like an account) owns the money associated with it. These keys are stored in what’s known as “wallets”, usually in the user’s computer or smartphone.
It presents several advantages over non digital currencies. It is not linked to its owner’s name, for example. Nobody can take it from you (as long as only you know the private key).
Anyone can use this system. Store owners can accept bitcoins as a valid payment for their products. Bosses can pay their employees with it. Speculators can try to make money playing with its value fluctuation and government-oppressed citizens can keep their money away from the corrupt law.
Bitcoin as a technology is a peer-to-peer, distributed system where a network of nodes running software that speaks the bitcoin protocol maintains a ledger known as the blockchain. The reference implementation of the bitcoin protocol is called Bitcoin Core, also known as “Satoshi client”.
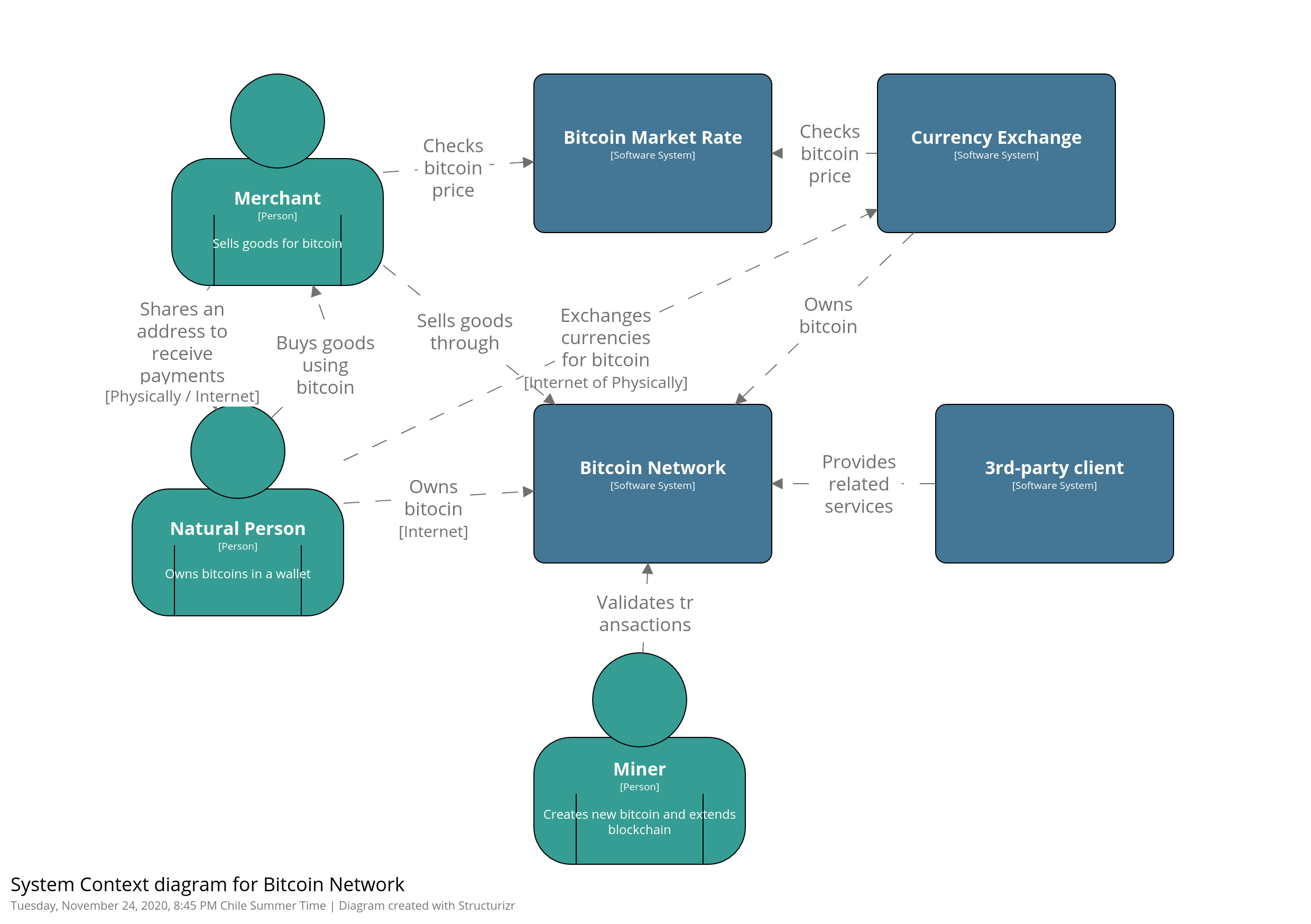
There are four main kind of users of the system:
-
Developers use the technology to provide and create new tools that interact with the Bitcoin network.
-
Miners verify and record transactions while solving a mathematical problem, creating new bitcoin.
-
Wallet owners make transactions (money transfers) with other users.
-
Exchanges who “exchange” real world currencies (like US dolar) for bitcoin.
A “bitcoin wallet” is the most common user interface to the bitcoin system, just like a web browser is the most common user interface for the HTTP protocol.
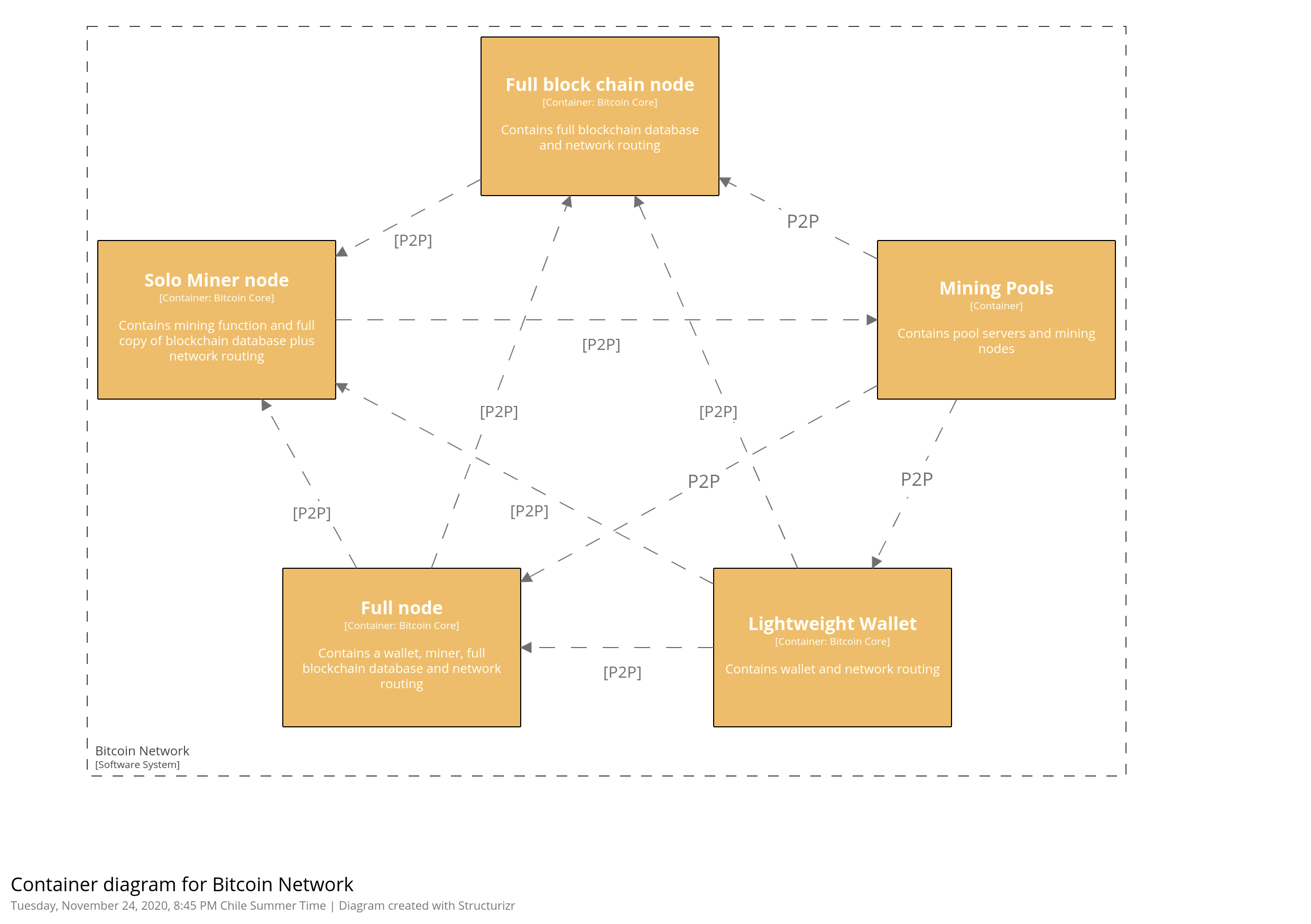
- Wallets (platform):
- Desktop Wallet
- Mobile Wallet
- Web wallet
- Hardware wallet
- Paper wallet
- Wallets (network)
- Full-node client
- Lightweight wallet
- Third-party API client
Visualization
Context Diagram
Container Diagram
Quality Attributes
-
Security
Security is about the capacity of the system to reduce the probability of malicious or accidental actions, resulting in loss or theft of valuable information, resources, assets, among others.Bitcoin uses modern cryptography to verify ownership of an account. Only the user, who has the private key associated with an address, can sign transactions, spending the money linked to it.
QA Scenario
“An unauthorized user tries to spend someone else’s coins. The transaction is considered invalid and it’s discarded from the next block”
Source: Unauthorized user
Stimulus: Creates transaction using other user’s address as input
Artifact: Mining node
Environment: Normal operations
Response: Transaction is not added to the next block.
Response measure:
-
Reliability
It’s about the ability of the system to continue to operate under unexpected circumstances. Bitcoin, being distributed, has no single point of failure. Each full-node contains the whole blockchain and propagates it and the new transactions to neighbor nodes in the network.
QA Scenario
“After an electric outage in a city, several Bitcoin nodes go offline and disappear from the network. The whole system continues working normally since there are other nodes available”
Source: Electric outage
Stimulus: Puts several nodes offline
Artifact: Bitcoin network
Environment: Abnormal operations
Response: The system keeps working
Response measure: No failing transactions
-
Usability
Usability is about how easy is for the user to accomplish an specific task with success. In Bitcoin there are several measures to minimize the possibility of errors while using the system, which increases the confidence and satisfaction of the user. This is important considering that transactions are irreversible.
QA Scenario
“Bitcoin user mistakenly enters a wrong character in the money recipient’s address. Since addresses have a checksum, the transaction is considered invalid and no money is lost”
Source: Wallet owner
Stimulus: Inserts a wrong character in output’s address
Artifact: Transaction validation
Environment: Normal operation
Response: Transaction cancelled
Response measure: No cost of error