VSCode — Overview
1. Description
1.1 Purpose of the system
The application is intended to be used for software development and general source code edition. Is a desktop application that works on Windows, Linux and macOS. The main characteristic of the application is its flexibility and extension availability, which makes the application very customizable, at the taste of the user.
1.2 System users
The application is mainly used by software developers that need a lightweight code editor. It is the most used code editor due to its flexibility and extension availability. Also, the Extension API, that provides functionalities for making other extensions.
We can recognize 2 types of users for the application:
- Normal users: also known as developers, are those who use the application for coding purposes. They know how to use the application and use the extension system for personalization.
- Extension developers: those who use the Extension API and develop extensions for the application. They may use the application for coding purposes but are diferenciated due its capabilities on extension development.
2. Visualization
The following diagrams describes 2 levels of the architecture of the system.
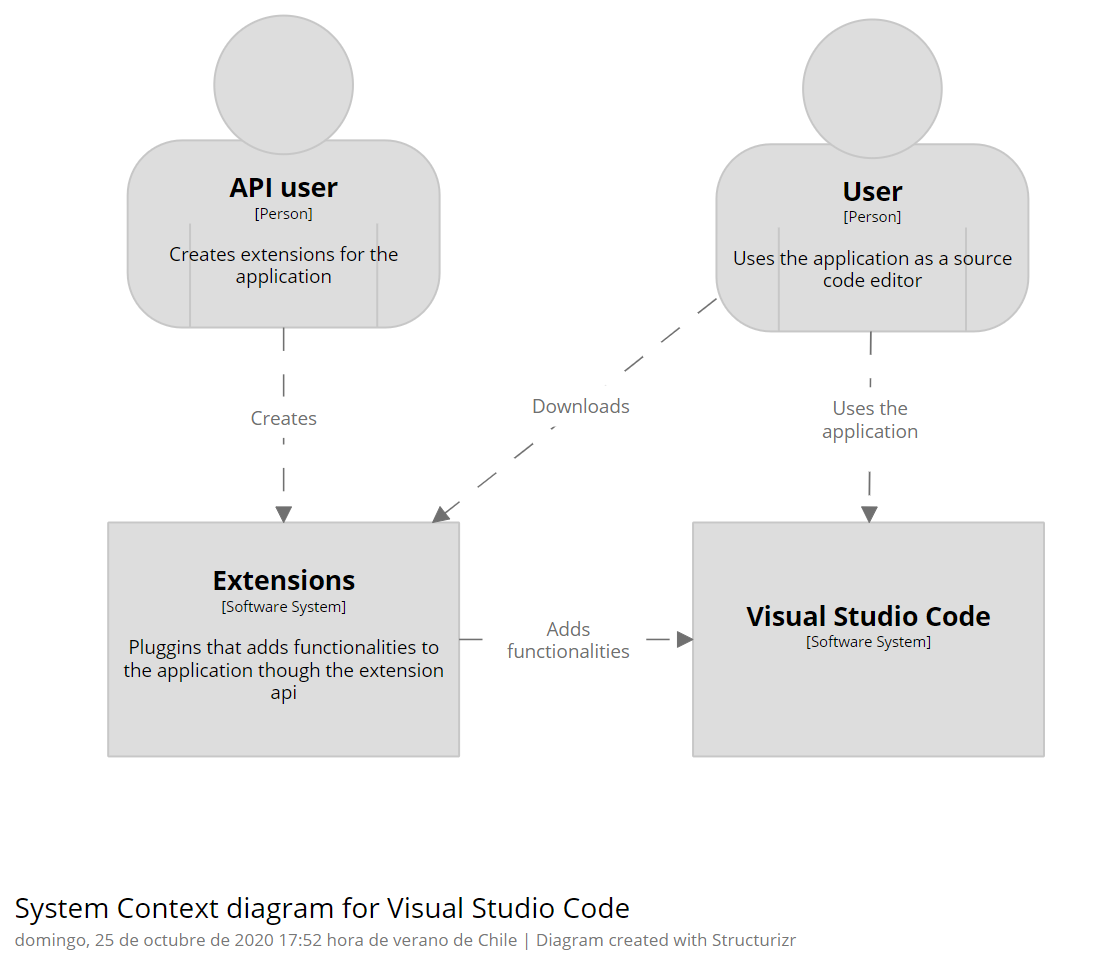

3. Quality Attributes
In the following section, three Quality Attributes are specified for VSCode and a QA scenario is developed for each one.
3.1 QA description
The 3 principal QAs for VSCode, based on our understanding of the system, are as follows:
1. Performance: VSCode stands out for being lightweight, and seeks fastness on the coding experience. The extensions of VSCode add functionalities, however, these run in different processes, so they decrease little or nothing the software performance.
2. Usability: this attribute, being one of the most important, stands out in VSCode. First of all, the application has a huge list of keyboard shortcuts (more can be added through extensions), which accelerate user interaction. Secondly, VSCode is available for Windows, macOS and Linux, i.e., the most used operating systems in the world. Also, it is easy to understand how to use it, where everything is, etc.
3. Flexibility: this text editor is built with extensibility in mind, which makes it very flexible, since extensions provide a lot and in a wide range of functionalities, ranging from improving the UI and UX to support a new programming language or debugging a specific runtime, among others.
3.2 QA scenarios
3.2.1 Performance
-
Scenario description: a full stack developer is programming both backend and frontend in VSCode, for which he uses multiple extensions at the same time. All the functionalities of the extensions work without slowing down the text editor.
-
Source: full stack developer
-
Stimulus/Event: developer write code both backend and frontend
-
Artifact: code editor
-
Environment: normal operation
-
Response: developer continue coding with all functionalities provided by extensions
-
Response measure: performance is not slowed
3.2.2 Usability
-
Scenario description: a experienced developer, for increase his speed in programming, configures multiple keyboard shortcuts in the preferences section of VSCode. The system adopt all the configurations making the developer able to use the shortcuts and write code faster.
-
Source: experienced developer
-
Stimulus/Event: configures multiple keyboard shortcuts
-
Artifact: preferences section
-
Environment: normal operation
-
Response: continues coding with new keyboard shortcuts
-
Response measure: new keyboard shortcuts are operating after few seconds
3.2.3 Flexibility
-
Scenario description: a Ruby on Rails developer that uses VSCode was asked by his supervisor to develop a simple JavaScript application using NodeJS and other tools based on JavaScript. The developer rapidly downloads several extensions at the same time and the extension system integrates them into the application, making the developer able to use new functionalities.
-
Source: developer
-
Stimulus/Event: developer requests for new functionalities
-
Artifact: extension system
-
Environment: normal operation
-
Response: continues to operate with new functionalities
-
Response measure: no downtime